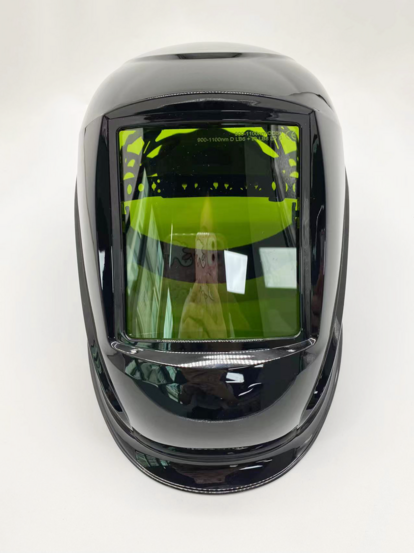
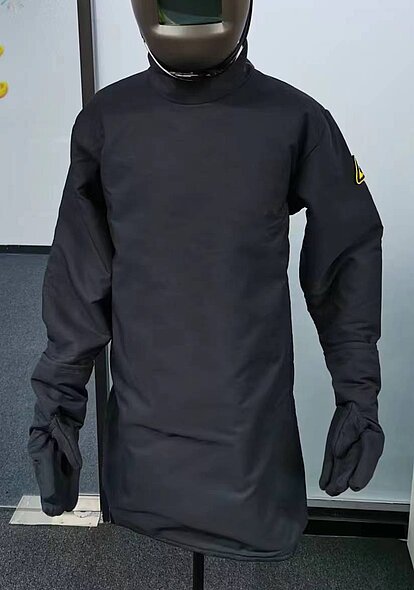
PhotonWeld Series: Your Safety and Health is our priority.
Make it also yours!
A laser is a device which produces an intense, coherent, directional beam of light.
The term LASER is an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Lasers can be designed to deliver a large amount of energy to a very small area. In laser welding and laser cutting operations, this energy can heat metals quickly to very high temperatures. Much of the radiation that strikes the workpiece can be reflected into the environment, creating hazards. Mostly laser light used in laser welding equipment is invisible for the human eye (INFRARED-A), so the hazard may not be readily apparent.
POTENTIAL HAZARDS of Laser Welding
Laser safety: Laser protection class 4 applies to all our manual laser welding equipment when in operation.
Different measures are therefore required on the customer side to ensure laser safety, such as:
- the appropriate training of employees,
- wearing special Personal protective equipment (PPE)
- setting up a separate laser safety area
New technologies, new challenges, new LASERMACH solutions.
When using handheld laser welding or laser cleaning machines, protective measures must be taken to protect the surrounding area and above all humans.
2010: LASER PROTECTION BECOMES A REALITY
Since October 2010 the “Occupational Safety Directive on Artificial Optical Radiation” (OStrV) has defined that: “Optical radiation is any electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range from 100 nm to 1 mm.” (OStrV BMdJ 7.2010) The range of optical radiation is divided into UV (ultraviolet: 100–400 nm), visible light (380–780 nm) and IR (infrared: 780 nm–1 mm ) (This last range we use for welding - 1076nm).
The directive provides protection against hazards in particular for the eyes and skin. It requires a professional risk assessment and corresponding protective measures wherever Class 3B, 3R and 4 hand-guided lasers are used (Sec. 3 of OStrV).
DISPERSE BUNDLED ENERGY
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and technical measures at the workplace protect against laser beams. In accordance with this, Lasermach supplies protective clothing, gloves, facial protection as well as protective curtains and machine covers Under the Brand PhotonSafe®.
SEPARATION OF LASER AREAS
According to the German Ordinance (which is taken as reference for Europe) on the Protection of Employees Against Hazards caused by Artificial Optical Radiation (OStrV), laser areas must be designed in such a way that the class 1 emission limit of the laser is never exceeded outside the defined laser working zones.
This condition can, for example, be met by means of large-scale mechanical shielding made of tested and certified material. For this purpose, Lasermach offers laser safety curtains, safety screens, manual or motorized rollers, fixed or roller-mounted screens, and screens for Laser welding, laser cleaning and laser cladding..
LASER WELDING SAFETY – WE TAKE IT VERY SERIOUS
You too have to take it VERY serious!
Laser radiation of infrared fibre lasers can cause serious and lasting damage to the human eye – so a handheld laser is not a toy. But simple precautions and our inherent safety design make this a safe solution that meets the requirements of globally active customers and their safety organizations.
Lasermach PhotonWeld© is a Class 4 laser system, requiring:
- Personal protection (laser safety eyewear)
- Safety curtains to block operating area from unprotected bypassers
- Laser safety officer (1 day training)
Lasermach offers superior laser safety:
- CE marking based on an in-depth risk analysis following Machinery Directive EC2006/42/EG.
- a true CE design according to machinery directive EC2006/42/EG
- Components with safety performance level D, including Safety PLC instead of custom control board
- Interface for connection of external safety devices (E-Stop, interlock and laser warning light)
Protection at laser Welding
Our Range of protection tools for Laser Welding radiation
Laser Welding Curtains - Flexible laser barriers
PhotonSafe Laser Welding protection Curtains - Laser Barrier curtains
The flexible Laser Safety Barrier is a flexible laser protective screen that has the characteristics of high laser protection level, flexible and convenient use, and high cost performance, especially suitable for large area area protection.
Laser Welding Shields/walls - Hard Laser Safety Barrier
PhotonSafe laser safety barriers - laser safety shields
The hard Laser Safety Barrier is assembled with a laser protection plate and an aluminum frame. It has the characteristics of high laser protection level and flexible and convenient use. It is suitable for high KW-level fiber laser protection, Safety protection for laser processing workshops, laser welding, cleaning and cladding equipment.
Laser Welding Windows - Laser Welding protection Windows
Laser safety window for laser welding machines
Our laser safety windows, specially designed to protect against welding-, cleaning- and cladding- lasers in various applications effectively.
Our Laser Welding Safety Windows are used to protect against lasers' radiation while still allowing good visibility.
CE Certified EN 207
Laser Window Foil - LASER WINDOW FILM
Laser protection foil to put on standard windows for full eye protection
The Lasermach Safety team is proud to provide a high-quality laser window film.
Laser Welding protection faceshields - Laser Safety Face Shields
Laser Welding protective face shields - Laser safety and protection face shield mask .
Combi welding & Laser Welding protection auto darkening faceshields - Laser autodark Safety Face Shields
Auto darkening Laser Welding protective face shields - Combi Laser safety and protection face shield mask for welding and laser welding.
Laser Welding Protection Clothing
Protective clothing for laser operators
Laser Welding Safety Signs - Laser safety signage
Laser Safety electronics- Laser safety controls
Laser safety signage is of crucial importance in all environments where the use of lasers is present.
Common Laser Hazards
One aspect to remember about laser welding safety is the variety of hazards associated with the systems which are also prevalent in many other forms of equipment. Basic safety training should mean workers are already familiar with some of these issues, but employers should be aware of:
- intense visible and invisible light
- Compressed gasses
- Intense radio frequency energy
Light Hazards
Due to the laser safety checks in place for welding systems, units are designed in such a way to prevent operators from coming into direct contact with the laser beam.
One of the issues that can arise, however, involves unintentional reflected light, which falls into the following categories:
- Diffuse Reflections – This type of reflection occurs when a reflective surface’s irregularities create a scattering of light in all directions. Of the types of reflections, this is the safer of the two since energy is being divided in many directions and weakened.
- Specular Reflections – This type of reflection is produced in a way that is more mirror-like, recreating close to 100% of the original light compared to the scattered light of diffuse reflections. Though there is a higher danger associated with this form, it is much less common and laser welding systems are often designed to eliminate specular reflective surfaces that would come across the beam’s path.
With proper safety procedures in place, and by following guidelines which accompany your laser welding systems, these hazards should be greatly minimized.
Skin and Eye Hazards
Due to laser engraving safety checks in place, the effects of lasers on skin are usually considered of secondary importance. Compared to laser welding and engraving systems, high-powered infrared lasers utilized in applications for welding and cutting pose a much greater risk of injury.
Some potential effects that can occur if safety procedures are not followed include mild reddening, blistering, and charring, all of which are usually reversible or repairable. Other potential issues could include ulceration, scarring of the skin, depigmentation and damage to underlying organs.
In regards to eye safety, some forms of laser beams operate at a wavelength which if exposed to the eye can pass beyond to the retina. With no pain indicators present and the beam being invisible, someone exposed can be unaware at the time of occurrence.
This is just another reason why utilizing industry-standard laser safety glasses is so vital to maintaining a safe and healthy workspace.
Electrical Hazards
An additional hazard that can be posed when using laser systems is that of electrical shocks. Some of the ways shocks can occur is through contact with:
- Exposed utility power utilization
- Device controls
- Power supply conductors operating at potentials of 50+ volts
Operators and service workers for laser welding systems must be especially careful to avoid these dangers by following standard safety protocols. These hazards could be experienced during:
- Set-up and installation
- Maintenance and service
- Troubleshooting, if equipment protective covers are removed
The electrical injuries that can be sustained from improper and haphazard use of laser systems can include everything from a slight tingle to serious bodily injury to death. To avoid accidental contact with these energized conductors, laser welding units utilize a barrier system within the equipment.
Safety Classifications
Depending upon the risk of a specific type of laser, it is graded from Class I to Class IV. Laser welding machines tend to be graded as Class IV lasers, making laser welding safety all the more important.
Two important additional classifications to keep in mind are the Maximum Permissible Exposure (MPE) and Nominal Hazard Zone (NHZ) designations.
- Maximum Permissible Exposure – This is the highest level of laser radiation an individual can be exposed to without receiving harmful physical effects to the eye or skin. Control measures for laser welding systems are in place to ensure any laser radiation emitted falls below the MPE.
- Nominal Hazard Zone – To create conditions for flexibility in laser welding applications, the laser beam of the unit is often not fully enclosed for practicality reasons. In these instances, it is necessary to define an area of potentially hazardous laser radiation, which is the NHZ. Control measures are then put into place for this area to ensure safety during use of the laser system.
Being fully aware of these classifications and their rationales are vital to ensuring proper workplace laser welding safety.
Safety standards for laser working places - Safety requirements and testing
Safety of laser products - Equipment classification and requirements
EN 12254:2010 => Laser Safety Standard NOT suitable for laser welding
Only for Labo use with laser power of maximum 100 Watt
This standard specifies functional requirements and a product labelling applicable to temporary and permanent passive guards (in the following called screens) for protection against laser radiation. This standard includes test methods for testing functional performance and the specification of the user documentation to be supplied with the product.
The screens are designed to protect the user from:
- unintentional exposure to direct and/or diffuse laser radiation;
- a time limited exposure to laser radiation, based on the functional requirements determined by risk assessment.
This standard applies to supervised screens for installations in working places at which laser radiation up to a maximum mean power of 100 W or single pulse energy of 30 J occurs within the spectral range between 180 nm (0,18 µm) and 106 nm (1 000 µm).
This standard applies to the protection against laser radiation only. This standard does not apply to other hazards including hazards from secondary radiation that can arise during, for example, material processing. like laser welding or laser cleaning.
EN 12254:2010 => Laser Standard NOT suitable for laser welding
Laser enclosures and housings that are supplied as part of the laser product or are supplied to be fitted to a laser system to form a laser product (according to EN 60825-1) are not considered to be within the scope of the standard.
IEC 60825-4:2022 - BS EN IEC 60825-4 - Safety of laser products - Part 4: Laser guards -->Laser safety standard suitable for laser welding
The only Acceptable Standard for Laser Welding Protection
IEC 60825-4:2022 deals with basic issues concerning laser guards, including human access, interlocking and labelling, and gives general guidance on the design of protective housings and enclosures for high-power lasers. Laser guards may also comply with standards for laser protective eye-wear, but such compliance is not necessarily sufficient to satisfy the requirements of this document.
This part of IEC 60825 specifies the requirements for laser guards, permanent and temporary (for example for service), that enclose the process zone of a laser processing machine, and specifications for proprietary laser guards.
This applies to all component parts of a guard including clear (visibly transmitting) screens and viewing windows, panels, laser curtains and walls. In addition, this document indicates
- how to assess and specify the protective properties of a laser guard, and
- how to select a laser guard.
IEC 60825-4:2022 => Laser Standard IS FULLY suitable for laser welding

Rules of conduct on the safe use of lasers
The following rules are of particular importance:
- Never point the laser beam at anyone’s eyes!
- Do not look directly into a laser beam!
- Always wear protection glasses!
- If the laser light accidentally strikes your eyes, close your eyes and immediately move your head out of the laser beam.
- Do not use any focusing optical device to look at the laser beam while working with lasers.
The Importance of Laser Danger Safety Signing and Marking
With the constant changes coming to the industrial and manufacturing sectors, and advanced equipment like laser welding systems becoming increasingly prevalent, it’s more important than ever to be aware of laser danger marking/indication safety procedures.
These procedures range from ways to protect from bodily harm while utilizing Laser Welding machines to ways to avoid electrical dangers on the factory floor. It’s important to know what all of these dangers are and how to train yourself and your staff in essential laser safety.
Air emissions from welding: radiation, fumes, dust
First of all, we need to talk about the most dangerous emissions into the atmosphere from welding, both for professionals and for those who use the finished product.
One of the most important risk factors for you, especially for operators, comes from the radiation emitted during welding: the most dangerous are ultraviolet radiation, as it is absorbed almost entirely by the skin and eyes. As Photonweld laser welding machines only use Infrared laser, this results in a minimal UV light generation and a minimal danger of UV damage. The protection of each exposed area is the most effective solution. Much les dangerous is the infrared light radiation.
Welding fumes, on the other hand, are a very different problem: the effect changes according to the welded metal, going from problems with the respiratory system to damage to the skeletal system. For this reason, during welding, the work area must be well ventilated, or equipped with the right suction machinery.
Another element that requires suction are the so-called welding powders, very small particles of material with high toxicity and capable of penetrating the respiratory system. Electrode welding has the highest concentration of dust among all welding techniques, so you need to protect yourself with a mask
INFRA RED HEAT RADIATION DANGER AT LASER WELDING
Danger of Laser radiation for the Eyes: Invisible Radiation from laser welding processes can seriously burn eyes an skin quickly and permanently.
Invisible Infra-red light radiation is used when laser welding. Due to the interaction with the workpiece, high levels of hazardous infrared-A and secondary radiation can produced by reflection. This light radiation is often reflected from the workpiece into the work area. Radiation from laser welding processes can seriously burn eyes an skin quickly and permanently.
The intensive fiber laser light radiate in the visible spectrum but invisible for humans, is especially dangerous to the eye. Fibre laser radiation penetrate through to the retina which can be destroyed irrevocably by relatively little radiation.
Misdirected laser radiation can come directly from the laser and threaten the eyes as a result of a faulty parameter setting, an opened cover, a displaced mirror etc. Other hazards include skin burn or inflammation from combustible materials as a result of misdirected laser radiation. The greatest hazard, however, usually stems from reflected laser radiation: the major share of the laser radiation is reflected by cold material first. To this we can add reflections of work piece edges, as a result of turbulence in the weld pool etc.
Misdirected radiation and reflections must be blocked off. That is why the law stipulates that the laser beam and the work zone must be in an enclosure. Beyond that, all those present, and the machine operators in particular, should wear protective goggles that are appropriate for the laser radiation being used. Fibre laser radiation are very dangerous to the eye and require special protective measures and approved safety goggles.
Safety for your EYES
Safety Eyewear for laser Welding
Our Selection of Special Laser Welding protection Goggles and faceshields
Check more on Safety for your Eyes - Check our Safety Eyeware
Standard protective welding goggles or sunglasses made of glass or acrylic glass are not suitable at all, as glass and acrylic glass allow fibre laser radiation to pass through!
FUMES, SMOKE AND MISTS DANGER AT LASER WELDING
Lasers easily melts, boils and vaporize metals. In doing so, fumes and mists are created which can present a respiratory hazard. Often the fumes and mists cannot be seen, yet they can pose a serious health hazard. Always use adequate ventilation.
Info on protection against fumes
FIRE DANGER AT LASER WELDING
Since the laser system produces a very small spot size with high energy, the hazard of fire is present if the beam hits flammable material. Keep flammables away from the welding or cutting area. Be sure to cover and protect anything flammable in the area, since reflected radiation could start fires in unexpected places. Protect the work area.

MECHANICAL DANGER AT LASER WELDING
If the the optical laser device is mounted on an robotic arm or other beam manipulator, these can malfunction and send the laser beam in unintended directions. Therefore, it is essential that the work cell be shielded in conformance with standards for the laser type and class.

ELECTRIC SHOCK DANGER AT LASER WELDING
Since lasers require a large amount of electrical power to accomplish specific tasks, electrical hazards are present. Conventional hazards associated with any electrical industrial power source are present. These require standards and common electrical safe practices as found in Safety and Health Fact Sheet . There are the unique electrical hazards common to lasers in general and the hazard of the individual application. Usually, the best source of safety information is provided in the instruction manual from the manufacturer of the laser system. Always read, understand, and follow the manufacturer’s recommended safety procedures.

A WORLD-CLASS LASER WELDING MACHINE MANUFACTURER

PhotonWeld Series: Full CE Safety certified Handheld Laser Welding Machines
Equipped with all CE requested Safety accesoiries connections as standard
- Laser beam Emission indicator + external emission warning indicator control
- Remote interlock connector with Multi safety interlocks:
- Nozzle contact interlock
- Door contact (external) interlock
- Foot pedal (dead’s men pedal) interlock (opt.),
- Hardware Key control lock
- Internal and external double wired emergency stop (opt.)
- Failsafe start-stop control
- Active Control of start and stop from external fume extraction system
WE HOLD SAFETY OF PEOPLE IN HIGH ESTEEM!

How to build a laser welding safe working zone in your workshop?
How to build a laser welding safe space in your workshop?
Class 4 Laser Operation Requirements for Safe Working
If you want to know how to make your safe laser welding zone:
Click here for info on laser safety cabins/laser safety rooms
Disclaimers:
(1) When buying laser safety products, please read carefully the products specifications, because of the specific laser-rated safety parameters for each product.We are not responsible for any accident caused by incorrect selection and use of products out of range of laser-rated safety.
(2) Laser operators should consider working environments, viewing conditions and beam delivery systems when making assessments and determining the correct laser safety products. Please consult with your laser safety officer or the third-party organization for correct equipment and use.
(3)All our products are designed and manufactured to prevent an occasional short time (in second) laser reflection and scattering. In any case, laser beam is interdicted to hit directly on person or laser safety products. We are not responsible for any accident due to incomprehension of laser hazard and nonobservance of laser safety standards and wrongful operation.