Sicherstellung der Qualität von Laserschweißnähten
Prozessspezifikation und Bedienerqualifikation für das Laserstrahlschweißen
Wie alle Schweißverfahren muss auch das Laserschweißen sorgfältig kontrolliert werden, um die Qualität sicherzustellen. Ein schlecht kontrollierter Prozess öffnet die Tür zu Rissen, Porosität, ungenügender Eindringtiefe und mangelnder Verschmelzung, die, wenn sie in ausreichender Menge vorhanden sind, zum Versagen der Schweißverbindung führen können.
Sie fragen sich vielleicht: „Diese Schweißnähte sind so winzig, wie um alles in der Welt soll ich ihre Qualität sicherstellen?!“ Die gute Nachricht ist, dass es etablierte Methoden gibt, um die Qualität von Laserschweißnähten sicherzustellen. Hier sind die drei, die ich für die wichtigsten halte:
1. Ein schriftliches, qualifiziertes Schweißverfahren
In der Welt des Schweißens dokumentieren Sie Schweißverfahren mithilfe einer Schweißverfahrensspezifikation (WPS). Ein WPS ist ein Dokument, das alle wesentlichen Variablen spezifiziert, die bei der Herstellung einer bestimmten Schweißverbindung definiert und kontrolliert werden müssen. Einige dieser wesentlichen Variablen sind Verbindungsdesign, Grundmetalltypen, Zusatzmetalltypen, Schutzgase, Lasertyp und Lasereinstellungen.
Ein WPS muss in der Regel durch Tests qualifiziert (oder nachgewiesen) werden. Dies umfasst in der Regel die Herstellung von Testschweißungen gemäß WPS und die Durchführung geeigneter Materialtests an den Testschweißungen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie alle technischen Anforderungen erfüllen. Zu den WPS-Qualifizierungsprüfungen können zerstörungsfreie Prüfungen (Sichtprüfung, Eindringprüfung, Röntgenprüfung, Dichtheitsprüfung) oder zerstörende Prüfungen (Biegung, Zug, Härte, Metallographie) gehören. Genaue Prüfanforderungen werden in der Regel in den Vertragsunterlagen (Konstruktionszeichnungen oder Qualitätsspezifikationen) festgelegt. Die Ergebnisse der WPS-Qualifikationstests werden in einem Procedure Qualification Record (PQR) dokumentiert.
2. Qualifizierte Schweißfachkräfte
Die Person, die die Laserschweißmaschine bedient, sollte geschult sein und ihre Fähigkeit nachweisen, Schweißnähte herzustellen, die den geltenden Qualitätsanforderungen entsprechen. Die Schulung sollte nicht nur die ordnungsgemäße Bedienung der Geräte umfassen, sondern auch die Sicherheitsaspekte beim Arbeiten mit Lasern.
Der Nachweis der Fähigkeiten des Bedieners umfasst in der Regel Tests, die der WPS-Qualifizierung ähneln. Die Bedienerqualifizierung kann je nach Vertragsanforderungen zerstörungsfreie und/oder zerstörende Prüfungen umfassen. Die Ergebnisse dieser Tests werden in einem Operator Process Qualification Test Record (OPQTR) oder einem ähnlichen Formular dokumentiert.
3. Qualitätsprüfung von geschweißten Produktionsteilen
Um die dauerhafte Qualität lasergeschweißter Teile sicherzustellen, sollte ein Hersteller über ein Qualitätssicherungsverfahren verfügen. Die Einzelheiten dieses Qualitätssicherungsverfahrens können von Organisation zu Organisation oder von Vertrag zu Vertrag variieren. Die meisten umfassen Probenahmepläne, Inspektionsverfahren, Akzeptanzkriterien und eine regelmäßige zerstörende Bewertung.
Das Laserschweißen bringt viele Vorteile mit sich.
Bei richtiger Steuerung können zuverlässige und qualitativ hochwertige Schweißverbindungen in Ihrem Produkt hergestellt werden.
This page is still under construction
ISO 15609-4:2009 - Specification and qualification of welding procedures for metallic materials
Welding procedure specification - Part 4: Laser beam welding
Abstract
ISO 15609-4:2009 specifies requirements for the content of the welding procedure specification (WPS) for laser beam welding processes, including overlay welding. It is not applicable to other processes for cladding (e.g. thermal spraying).
Variables listed in ISO 15609-4:2009 are those influencing the quality and properties of the welded joint.
This standard was last reviewed and confirmed in 2020. Therefore this version remains current.
Laser Welding Quality Related to Penetration
Penetration depth and penetration defects at laser Welding
The penetration depth is closely related to the joining strength. Any penetration defects on welds, such as inappropriate relationships between the penetration depth and base material, will greatly affect the quality and strength of welding. With butt laser welding as an example, the following describes typical penetration defects.
Insufficient penetration
A defect where the amount of penetration is insufficient compared to the required penetration depth due to factors such as insufficient application of heat to the molten metal. The figure shows an example of lap fillet welding. In butt welding, this defect easily occurs on the bottom of grooves. In the case of a thin plate tee (horizontal fillet) coupling, penetration is regarded as insufficient if the penetration depth is 20% or less of the thin plate.
Incomplete fusion
A defect in which parts of the base metal have not been penetrated by the molten metal. The figure shows an example of a thin plate tee (horizontal fillet) coupling. This defect is caused, for example, by the insufficient application of heat to the molten metal and pre-flow of molten metal. In circumferential welding, it is also caused by the preceding and succeeding beads being transferred to lap welding before they have penetrated sufficiently.
Photonweld laser welding quality inspection tools
Photonweld quality inspection tools
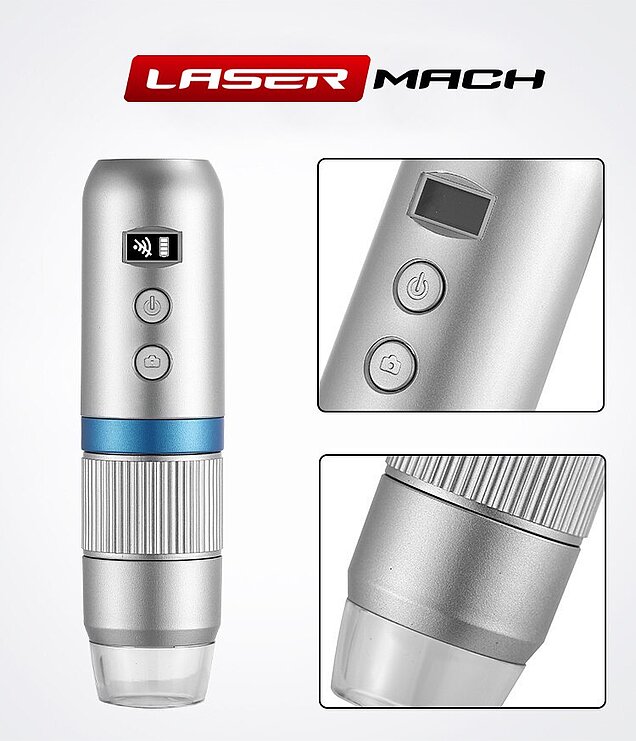
Photonweld laser welding inspection microscope

Portable Digital Laser Welding Microscope
Optical Size: 1/4″
Magnification: 50X-1000X
Focus Range: 10~40mm
Sensitivity: 4300mV/lux-sec
Resolution: 640*480, 1280*720, 1920*1080

Portable Digital laser Welding Microscope
A compact digital microscope for quality control of laser welded parts with versatile connectivity options such as WIFI and USB is available. This device can seamlessly link to phones, tablets, laptops, and PCs, displaying images directly without the need for direct observation. Using the accompanying app, capturing photos and videos is straightforward, and the images can be easily saved.
The Portable Digital Microscope boasts comprehensive functionality, delivering clear imaging with meticulous craftsmanship. It features a built-in battery, facilitates computer connections and is compact and portable.
This portable digital microscope finds besides laser welding quality inspection, extensive applications across various fields, including electronic circuit board testing, industrial assessments, textile examinations, clock and mobile phone maintenance, skin and scalp inspections, printing assessments, educational and research purposes, precision object amplification measurement, aiding in reading and serving as a valuable tool for hobbyist research.
The welding procedure and its quality is dependent on ensuring that every step is done correctly. It is a technical task that requires proper certification, safety regulations, and training. Any damage to the welding part can be costly and might cause permanent structural damages to the final product.
Welding is a part of many industries such as construction, aviation, automotive, and more, and each of them demands quality assurance. Ensuring everything is welded perfectly together beforehand will protect you from hazardous incidents that can often take lives. Therefore, if you are thinking about hiring a welding service, make sure to receive the service from a reliable welding specialist who knows how to do this job.
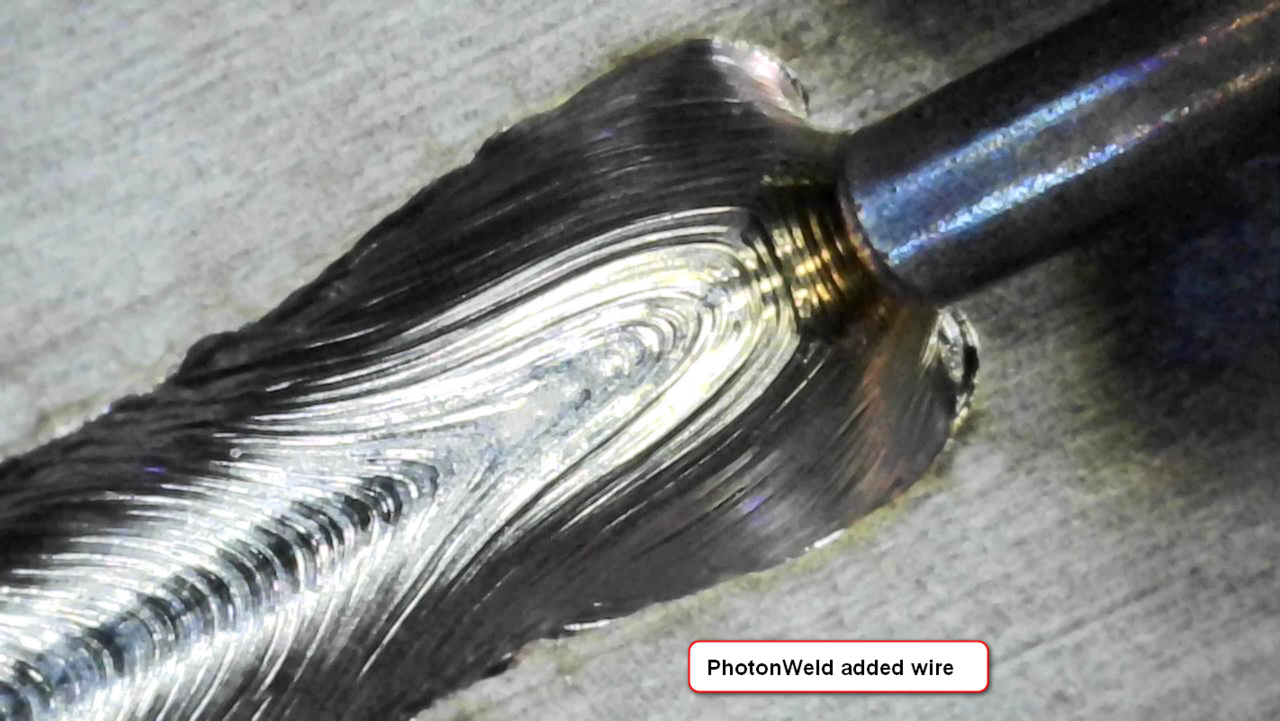



Full penetration laser welding, partial penetration laser welding, and their strength
Different grooves also cause different patterns of penetration, leading to differences in the strength of welds.
Full penetration laser welding
Full penetration welding is a welding method in which the groove of the base material to be joined is united and embedded with molten joining materials (filler rod and welding wire), as with butt welding.
It can be said that full penetration welds are highly reliable in strength design as they have the same proof stress as the base material. On the other hand, they require high welding quality. Particular attention is required at the ends of welds to prevent defects such as undercut welds. It is also important to control and adjust reinforcement because stress concentrates on excessive reinforcement, causing cracking or other such problems.
Partial penetration laser welding
Partial penetration welding is a method in which a partial groove is created on the base material. In this method, the base material is only welded partially, while full penetration welding welds the entire plate thickness of the base material. Although full penetration welding is used in general, partial penetration welding is required in some cases, such as where joined sections are intertwined due to the design and manufacturing of materials.
However, caution is required during partial penetration welding on locations to which bending moment or tensile force is applied because the welding strength of partial penetration welding is often not sufficient. Thus, the strength design of welds, as well as the measurement and inspection of whether dimensions of actual weld penetration such as throat thickness satisfy the design conditions, are all particularly important.



